반응형
for문과 while문의 차이
- for문은 루프를 도는 횟수가 정해져있음. 횟수 중심!
- while문은 조건 중심이다.
** 1부터 5까지의 합 구하기 예제
// while 문
int sum1 = 0;
int i = 0;
while(i <= 5) {
sum1 += i;
i++;
} System.out.println("1~5의 합: " + sum1); //1~5의 합: 15
// for문
int sum2 = 0;
for(int j = 1; j <= 5; j++) {
sum2 += j;
} System.out.println("1~5의 합: " + sum2); //1~5의 합: 15
** 1부터 100까지의 합 구하기 예제
//for문
int sum = 0;
int i = 0;
for(i=1;i<=100;i++) {
sum += i;
} System.out.println("1~" + (i-1) + " 합 : " + sum); //1~100 합 : 5050
//while문
int sum = 0;
int i = 1;
while(i <= 100) {
sum += i;
i++;
} System.out.println("1~100의 합: " + sum); //1~100 합 : 5050- for문에서 ( i - 1 ) 인 이유 : for문을 빠져나온 순간 i 값은 101이므로 100이 나오게 하려면 i-1을 출력해야함
** 구구단 출력하기 예제
for (int m=2;m<=9;m++) {
System.out.println("\n*** " + m + "단 ***");
for (int n=1; n<=9;n++) {
System.out.printf("%d x %d = %d\n",m,n,(m*n));
}
}
** 구구단 출력하기 예제 - 가로로 추출 (MultiplicationExample 예제 변형)
//구구단 가로로 추출
int i = 2;
for (int j=1;j<10;j++) {
for (i=2; i<10;i++) {
System.out.print(i + " x " + j + " = " + (i*j) + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
// System.out.println("\n*** " + m + "단 ***"); 해결
while문
- 기본적인건 위에 for문과 비교하면서 다루었음
** 바깥문 for문 종료
Escape: for(char upper='A'; upper<='Z';upper++) {
for(char lower='a';lower<'z';lower++) {
System.out.println(upper + "-" + lower);
if(lower=='g') {
break Escape; // 이름은 아무렇게나 지어도됨
// 소문자가 g가 되면 바로 Escape가 써있는 곳으로 탈출하겠다는 의미
}
}
}
System.out.println("프로그램 실행 종료");
continue
- continue문은 필터링을 해줄 때 사용한다
- 홀수일때는 다음으로 넘어가는 이 예제를 떠올리자
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) {
if(i%2 != 0) {
continue; // 홀수일때는 continue를 이용해서 넘어가게 하자
}
System.out.print(i+" "); // 2 4 6 8 10
}
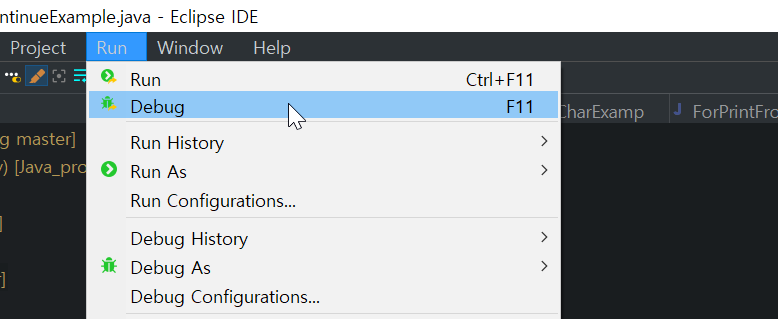
디버깅
- 디버깅 하는법 : run > debug 또는 벌레 아이콘 클릭
반응형
'👨💻 2. 웹개발_Back end > 2-1 Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [이클립스] 한글 깨짐 현상 해결 (0) | 2021.07.29 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] 05-1 참조타입과 참조변수 (0) | 2021.07.28 |
| [JAVA] 04-1 조건문 (if문, switch문) (0) | 2021.07.27 |
| [JAVA] 03-2 연산자의 종류 (0) | 2021.07.26 |
| [JAVA] 03-1 연산자와 연산식 (0) | 2021.07.23 |




댓글